
5 Menopause Support Complex Supplement to Help Ease Symptoms
Menopause support complexes are dietary supplements with herbal extracts and vitamins aimed at alleviating symptoms during menopause
Low blood sugar — also called hypoglycemia— is a serious concern that can wreak havoc on your overall health and wellbeing if left untreated. That’s why we’re going to provide insight into low blood sugar levels, how they can adversely affect your health, what to look out for, and steps you can take to maintain healthy levels.
Whether you’re more prone to low blood sugar levels due to a medical condition like diabetes, or simply looking to be more informed about potential symptoms to look out for, we’ll arm you with the knowledge you need to understand and take action on the matter. So let’s dive in to finally let you take control of vigilance for your own health.
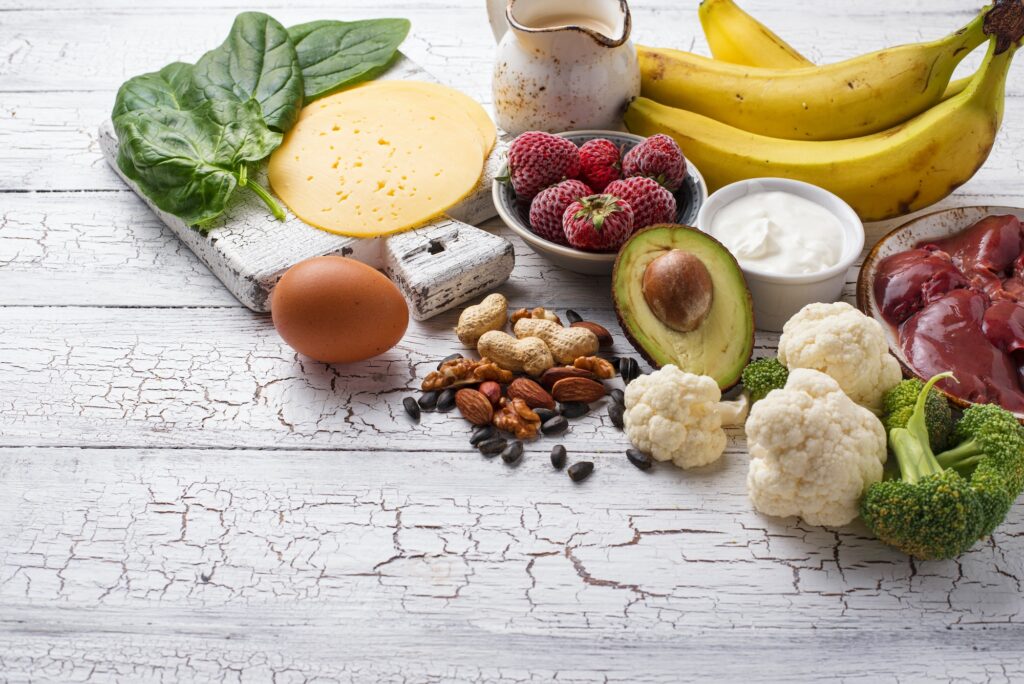
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is essential to one’s overall wellbeing. But what exactly is the normal range of blood sugar levels for a human? According to medical experts, the acceptable level is between 70-99 milligrams per deciliter before meals and 70-140 milligrams per deciliter two hours after meals. These values can still vary depending on factors such as age, activity level, stress levels, and health conditions such as diabetes.
It can be argued that anything above or below the aforementioned ranges should not be considered “healthy” given that it can lead to potential issues with one’s health down the line. Evidence from a 2019 study done by the National Institute for Health suggests that extended periods of time with high or low blood glucose can lead to chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes or even kidney failure in some cases.
Making sure to maintain a healthy range of blood sugar levels is key to maintaining one’s overall health and wellbeing. From this discussion, we can now look closely into how exactly low blood sugar levels – below 70 milligrams per deciliter – can impact one’s body and what treatments may be available in worst case scenarios.

Low sugar levels can have a significant impact on your health and wellbeing. Hypoglycemia, or having a low level of glucose in the blood, is a condition that causes a person to feel tired, weak, hungry, and possibly confused or dizzy. It can occur when someone with diabetes does not manage their diet or exercise correctly, or if they take too much insulin. Low sugar levels can also be caused by heredity, disease processes such as liver failure, some medications, and even excessive alcohol consumption.
It is important to differentiate between what is usually considered ‘normal’ blood sugar levels for humans and those that indicate hypoglycemia. While normal blood sugar ranges from 70 to 120 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter), some doctors may consider lower or higher values depending on individual cases. Hypoglycemia levels are generally recognized as being below 70 mg/dL. At such low levels, a person may experience symptoms related to the decrease in available energy within their cells and it is important that these levels are corrected rapidly.
The effects of hypoglycemia can range from mild to more serious, so it is important to seek medical advice if you consistently experience abnormally low sugar readings. In addition to feeling light-headed, anxious or shaky, signs of an adverse reaction may include tingling around the mouth or lips; sweating; intense hunger; dry mouth; blurred vision and headaches.
Having said that, there are many people who have been able to maintain healthy blood sugar levels despite lifestyle factors that one would expect would cause considerable drops in sugar for most individuals. This demonstrates that individual bodies react differently to various elements of our lives. Clearly then, there can be different interpretations of what constitutes ‘normal’ depending on context and physical characteristics.
Recognising how one’s own body responds is therefore essential in order to ensure healthy functioning of internal processes – this also applies to glucose levels in the blood which directly impacts our physical wellbeing. Assuming no sign of illness is present then subtle yet persistent adjustments in food intake aimed at moderating sugar levels may be necessary in order for individuals to achieve satisfactory results during home monitoring tests.

Physical Effects of Low Sugar Levels
Physical effects of low sugar levels on your health and wellbeing can range from mild to severe, depending on how long the person has been experiencing hypoglycemia. Most often, symptoms of low blood sugar include dizziness, headaches or feeling faint. Other physical symptoms may include sweating, trembling or feelings of anxiety. In more extreme cases, people may experience blurred vision, exhaustion and confusion.
The severity of these physical effects can depend on an individual’s overall health and how quickly they take action to combat their low sugar levels. For example, if a person with diabetes notices that their blood sugar levels are too low, they should immediately consume foods or drinks rich in carbohydrates in order to replenish their sugar levels (2). Doing so within a timely manner can greatly reduce the severity of any physical symptoms as well as preventing any long-term damage to the body.
There is also relatively strong evidence that links factors such as genetics and insulin resistance to developing type 2 diabetes, which suggests that those who have diabetes in their family may be at a greater risk for experiencing the physical symptoms associated with low blood sugar levels.
Though there is evidence that explicitly links low blood sugar levels to physical symptoms, some evidence has also been produced which says otherwise. Certain studies state that it’s not necessarily hypoglycemia itself that causes these physical effects but rather the prevalence of stress associated with it. The results of these studies are inconclusive however so further research is needed to determine whether or not this theory holds any merit.
In either case, however, it’s important for anyone who experiences frequent fluctuations in their blood sugar levels to pay close attention to their bodies and seek out medical help when necessary. Doing so will enable them to receive appropriate treatment from a professional and ensure that their overall health isn’t negatively impacted by low blood sugars over time.
With all the potential physical effects of low blood sugar considered, it’s just as important to consider how they affect us mentally and emotionally. Next we will discuss how hypoglycemia may influence our mental wellbeing.
It is well-known that fluctuations in blood sugar levels can have an adverse effect on physical wellbeing, yet little knowledge exists on the impacts on mental health. With much debate surrounding this topic, it is important to consider both sides of the argument.
On one hand, multiple studies have reported no correlation between low blood sugar levels and depressive behaviors or cognitive decline. One prominent study by Western Australian researchers looked into the relationship between diabetes and depression in 1,372 adults with type 2 diabetes. Upon analysis, they concluded there was “no association between persistent long-term hypoglycemia (blood glucose level <3.3 mmol/L) over a 5-year period and risk of depression”. This suggests that instead of being depressed due to low sugar levels, people with depression may rather act in ways that cause their blood sugars to drop.
However, other research has linked the two conditions directly. A closer look at the same study revealed current hypoglycaemia which had occurred shortly before the time of assessment was associated with higher scores on depression surveys. Additionally, a 12-month prospective study published earlier this year also supports this claim by stating ketoacidosis episodes were associated with greater severity of anxiety and depression. Given these findings it could be argued people who experience frequent and severe hypoglycaemia are more likely to experience mental health problems when compared to those with typically regulated blood sugar levels.
Despite the conflicting evidence, there is evidence to suggest certain individuals might be at risk of developing mental health issues due to low sugar levels. To better understand how these individuals can maintain healthy sugar levels and combat any potential detriment to well-being, we must first gain insight into how best to increase them.

Now that the mental effects of low sugar levels have been discussed, it is important to know how to increase sugar levels in order to better maintain your health and wellbeing. Lifting your mood when sugar levels are low requires precise balance and moderation. There is an ongoing debate over whether simple carbohydrates like sweets or foods with artificial sugars should be used as a method of increasing sugar levels.
On one side of the argument, it can be argued that any type of carbohydrate can help raise blood glucose levels and restore balance in the body; however, it can also be argued that simple sugars offer little or no nutritional benefit and may imply unwelcome health consequences such as weight gain or an increased risk of diabetes. Though these arguments both hold merit, much evidence supports that incorporating complex carbohydrates into a balanced diet is an effective way to manage symptoms associated with hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Complex carbohydrates contain fiber, vitamins and minerals which provide nutritional benefits and help sustain energy production for longer than regular sugars. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy diet with balanced servings of fruits and vegetables is another key factor for increasing sugar levels naturally.
To sum up, restoring balance within your body’s sugar levels requires both moderation and knowledge of what to consume. Eating small snacks throughout the day composed largely of complex carbohydrates such as brown rice, quinoa, oats or sweet potatoes is most likely going to provide the best health-related outcome.
Now that we understand how to increase sugar levels, let’s move on to discuss how following a nutrition plan grounded in balanced eating habits provides long-term improvements in our overall well being.
Nutrition and Balanced Dieting is an essential part of managing low blood sugar levels. Eating a balanced and nutritious diet allows for steady maintenance of glucose levels in the body, reducing the chance of spikes and crashes. And, as we previously discussed, having sugar quickly available when necessary helps to ensure that your body has what it needs to maintain healthy glucose levels.
When it comes to nutrition and balanced dieting, there are two sides that one can take: one side argues that eating healthy is key to managing low blood sugar levels, and the other side that believes moderation is important. Supporters of the eat healthy view might recommend focusing on low glycemic foods such as whole grains, nuts, fruits and vegetables; avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks; and limiting alcohol consumption. On the other hand moderates believe that although eating a healthy and balanced diet is essential for general health, it is possible to still enjoy treats when necessary.
Evidence shows that both sides may be right. For example, some research suggests that people who experience hypoglycemia should rely heavily on complex carbohydrates to maintain a steady energy throughout their day. However, others suggest that under certain circumstances allowing yourself to be treated so often can help reduce cravings and support long-term balance and wellbeing. If you do want to indulge, try eating smaller portions of sweets or replacing sugary snacks with healthier alternatives such as fruit or dark chocolate.
No matter which approach you decide works best for you, remember to always pay attention to how different foods make you feel in order to develop an idea of what works best for your body specifically. Taking small steps towards improving your nutrition will lead to long term better health outcomes and more control over your health as well as improved wellness overall.

Lifestyle Changes to Increase Glucose Levels
When discussing lifestyle changes to increase glucose levels, it is important to remember that balancing one’s diet, exercise and other lifestyle factors can have a profound impact on the body’s health and wellbeing. For individuals experiencing hypoglycemia – or low blood sugar – specific lifestyle modifications can help support healthy glucose levels.
One of the most effective strategies for restoring balance is eating a variety of healthy foods and snacks throughout the course of the day. Incorporating lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, nuts, and whole grains can be beneficial in helping individuals maintain steady energy levels and manage hunger cravings. Eating frequent meals every few hours may also help to reduce the risk of dangerously low blood sugar levels. Additionally, reducing the consumption of refined carbohydrates and added sugars in snacks and beverages can be helpful in more ways than one, as maintaining consistent glucose levels is essential for overall wellness.
Exercise has been found to play an integral role in helping individuals alleviate the symptoms of hypoglycemia. Working out regularly can assist in counteracting low blood sugar by stimulating the release of stored glycogen from the liver into the bloodstream. For those struggling with hypoglycemia, engaging in moderate amounts of physical activity every few days may prove beneficial in aiding their condition.
The use of dietary supplements have also been studied as a possible solution when attempting to normalize glucose levels. Vitamin B12 specifically has been found to assist individuals with hypoglycemia through its effects on modulating red blood cell production and functioning. However, before adding any supplement to one’s daily regimen it is imperative to consult a physician or nutritionist so as to avoid any potential adverse effects that could arise from their use.
Ultimately, improving current lifestyle habits such as nutrition, exercise, and stress management could aid those with hypoglycemia in achieving healthy ranges for their blood sugar levels. Thereby allowing them to experience improved wellbeing both physically and mentally – which are necessary for long-term success with managing chronic conditions such as hypoglycemia.

Turmeric, a yellow-colored spice commonly used in many cuisines around the world, is earning increasing interest for its potential health benefits. Scientists have been exploring these potential benefits for decades and are continuing to uncover more evidence supporting its use in medicating certain ailments.
Potential Anticancer Properties
Studies on laboratory animals suggest that curcumin, the active ingredient of turmeric, could be beneficial in reducing cancer risk. A study conducted by scientists at MD Anderson Cancer Center found that curcumin was effective as a chemopreventive agent against squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC) both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, studies suggest that curcumin may cause changes in cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, which results in cell death. These changes can potentially lead to the prevention or inhibition of tumor development.
Effects on Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the body’s normal immune response and occurs when tissues are injured due to damage or diseases like arthritis or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Studies suggest that turmeric has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation related to diabetes and high cholesterol due to its antioxidant activity.
Heart Benefits
There is insufficient evidence to say that turmeric is a reliable supplement for preventing heart disease and stroke. However, one study suggests that long-term supplementation may reduce cholesterol levels, which is likely due to turmeric’s anti-inflammatory properties. Further research is needed to confirm this benefit, but reducing inflammation is generally beneficial for avoiding heart problems.
Skin Health Benefits
Since ancient times turmeric has been used as a traditional skin remedy to treat conditions such as acne, psoriasis, eczema, dark circles under the eyes and wrinkles due to its antioxidant activity. It is also known for healing wounds quickly by decreasing inflammation and stimulating collagen synthesis. However, further research is necessary before specific recommendations can be made regarding the use of turmeric for skin health.
Brain Health Benefits
Recent studies have found that regular consumption of turmeric oil helps improve learning, memory recall and cognitive function in healthy animals as well as those with Alzheimer’s disease or dementia. This supports earlier findings indicating that curcumin plays a role in protecting nerve cells from damage while increasing blood flow to the brain; both effects help improve cognitive functioning overall.

Menopause support complexes are dietary supplements with herbal extracts and vitamins aimed at alleviating symptoms during menopause

Vitamin C, D3, Zinc, and Quercetin support immune health. They enhance immune cell function, fight infections, reduce inflammation, and provide antioxidant benefits.

Ginseng, a valued herb with adaptogenic and antioxidant properties, is popular as a supplement for improved well-being, energy, and immune function.

Nootropic supplements enhance focus, memory, and cognitive function. They boost mental clarity, motivation, and creativity for improved performance and brain health.

Garcinia cambogia, a tropical fruit, is touted for weight loss. Its active ingredient, HCA, may inhibit fat formation, but evidence is limited. Consult a professional before use.

More and more people are jumping on the mushroom supplement bandwagon these days, but you should be aware that there are potential side effects you should know about before taking the plunge. Whether you’re begging for overall well being or looking for an extra performance boost, you’re going to want to make sure you’re making an informed decision before adding mushroom supplements to your daily routine. We’ve put together a list of potential side effects to look out for, so read on and learn the truth before you start popping those pills.

Moringa, the “miracle tree,” offers numerous benefits. Moringa supplements provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory effects, and potential blood sugar and cholesterol regulation. They support immunity and combat malnutrition, but medical advice is essential.
It’s a good thing that Mother Nature both created and found cures for many of the ailments we humans suffer from. From the common cold to serious diseases, herbs have the potential to not only alleviate symptoms, but to completely prevent illnesses in the first place! Herbal remedies for immune system support have become increasingly popular as natural ways to boost your immunity against illness start to catch on.
