
5 Menopause Support Complex Supplement to Help Ease Symptoms
Menopause support complexes are dietary supplements with herbal extracts and vitamins aimed at alleviating symptoms during menopause
You don’t need to be a neuroscientist to recognize the connection between diet and the health of the brain – whatever you put in your body affects your overall well-being, including the function of your brain. If you’re looking for tips on how to keep your brain healthy with the foods you eat, you’ve come to the right place. Here’s how you can use the diet for a healthier, sharper brain.
Eating a nutritious and balanced diet plays an important role in maintaining healthy brain function. Foods packed with antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and B vitamins may also help with improved cognitive performance and overall mental health.

The direct connection between diet and brain food is becoming increasingly clear. Studies have confirmed that certain dietary patterns are associated with improved cognition, prevention of brain fog, and a reduced risk of dementia later in life. Conversely, poor diet has been linked to cognitive decline and increased risk for neurological diseases.
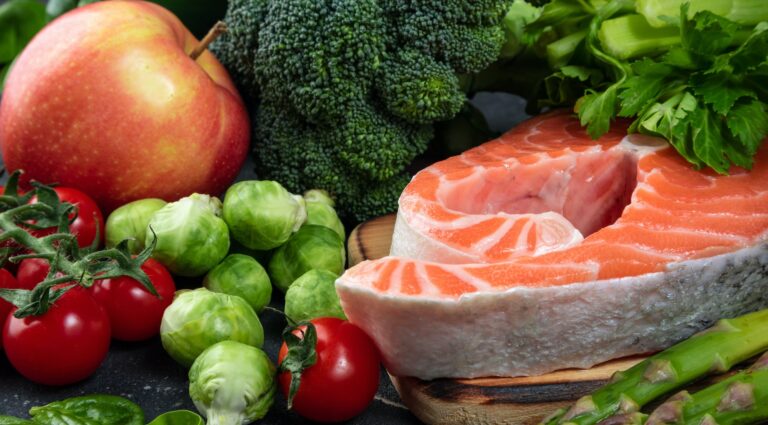
On the one hand, research shows that a healthy diet consisting of balanced meals containing fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can have profound positive effects on mental performance and reduce the chances of developing age-related dementia. Foods rich in omega-3, such as salmon or nuts, provide needed energy to the brain while allowing neurons to function more efficiently. Consuming these types of foods can also help regulate mood hormones such as serotonin which may help boost overall mental well-being.
There is evidence that aging brains may benefit from higher intakes of protein and fat rather than carbohydrates. Additionally, some high-fat or high-sugar diets may confer short-term cognitive improvements by providing an immediate energy boost to the brain. While this energy boost may be beneficial in the short term, it generally comes at the expense of long-term cognitive damage due to poorer overall dietary habits.
When it comes to boosting neural functions, your nutritional intake plays a major role. The human brain requires essential vitamins and minerals for proper functioning, so ensuring that your diet contains plenty of these key nutrients is essential for peak brain performance.
One key mineral with established links to improved cognition is omega-3 fatty acids, found primarily in fatty fish like salmon, tuna, mackerel, and sardines. Omega-3s are important for brain development, improved memory and concentration, and better vision. Other good sources of omega-3s include flaxseed oil, chia seeds, walnuts, and egg yolks.
Another important vitamin for healthy brain function is vitamin B12, which helps promote normal nerve functioning, as well as improve memory and focus. B12 is found in protein-rich food sources like beef, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products. If you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, B12 can also be found in fortified cereals and some nutritional yeast products.
Magnesium is another important mineral for mental performance. It assists with calcium absorption, helping to reduce stress hormones while promoting dopamine levels in the body. Good dietary sources of magnesium are dark leafy greens such as spinach and Swiss chard; nuts such as almonds and cashews; beans and legumes; bananas; avocados; whole grains such as quinoa or oats; fish; and dark chocolate.
Finally, zinc plays an essential role in learning processes by aiding communication within the neurons of the brain. Foods that are high in zinc include oysters, lean meats such as beef or lamb; yogurt; wheat germ; oats; milk and cheese; almonds; cashews; chickpeas; black beans; sunflower seeds; pumpkin seeds; quinoa; kale, and mushrooms.
By focusing on these key supplements along with other natural whole foods like fruits and vegetables that are packed with antioxidants, we can prepare our bodies to tackle the demands of daily life through improved focus and concentration levels. This leads us now to look closer at the potential cognitive benefits of a healthy diet.
Food is essential for optimal neuro-functioning and cognitive performance. Consuming a balanced and nutritious diet has been linked to improved cognitive performance in the form of better memory, concentration, and general learning ability. Studies have shown that specific supplements play important roles in cognition and that many dietary components and features are associated with enhanced mental abilities. Eating unhealthy processed foods can inversely affect learning and understanding, leading to poor concentration and overall lower intelligence. By consuming a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals, you can improve your overall cognitive performance.
According to a 2018 study, diets high in processed foods and sugary drinks were associated with an increased risk of developing dementia.
Mental performance relies on fuel from food, just like any other physical activity. Eating nutritious foods helps protect your brain, which can affect mental performance, sharpness, and memory recall.
Research has linked eating certain foods to improved mental function, suggesting that the food individuals consume can directly impact overall health, mental clarity, and alertness. Foods high in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts may be especially beneficial for mental focus and agility. Additionally, healthy fats found in things like fish oil and salmon help with cognition, such as mood regulation and focus. Protein-rich foods also provide energy for the mind and body, helping you stay alert throughout the day.
On the other hand, research has shown that consuming unhealthy foods such as processed foods high in sugar can lead to a decrease in cognition. This is because these processed foods can decrease levels of vitamins, minerals, and blood glucose levels that are necessary for optimal brain performance. Additionally, trans fats have been linked to disruptions in short-term memory and learning abilities due to their inflammatory effect on the body and brain.
Ultimately it is important to pay close attention to your diet to optimize your mental performance and sharpness. Eating a variety of wholesome foods throughout the day can help keep your brain fueled so you can think clearly and stay sharp. As we move on to the next section about how diet impacts mental illness it is also important to remember that good nutrition is essential for mental wellness too.

Mental illness has been linked to nutrition and diet for decades, though the role of diet remains mostly unexplored. Emerging evidence suggests that certain dietary components may play a role in mental health. A growing body of research has found a potential link between what we eat and our risk of developing certain mental illnesses.
An unhealthy diet can influence mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety, while their symptoms can be made worse by a poor diet. Unhealthy foods have been linked to an increase in depression, bipolar disorder, and other psychiatric disorders, indicating the importance of healthy eating practices when it comes to mental health. Diet can also affect cognitions such as memory and focus. Studies suggest that unhealthy foods are associated with poorer cognition and that consuming more best brain foods can improve many aspects of cognitive performance.
Some studies suggest that there is an association between a Western Diet — which is typically high in processed meats, refined grains, fatty proteins, and sugary beverages — and an increased risk of mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. However, other studies have shown conflicting results with no clear consensus on the matter. Additionally, other research indicates that dietary patterns may impact not just mental health but also physical health. Despite some promising research on the connection between nutrition and mental illness, further clinical trials are needed to establish a definitive link between specific diets and mental illness.
Evidence suggests that what we eat has a direct impact on our optimal health. Studies are increasingly finding links between diet and various forms of brain pathology, such as dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, Parkinson’s disease, depression, and psychiatric problems like schizophrenia. Researchers suggest that maintaining a healthy diet can reduce the risk of these conditions and may even slow their progression.
For example, diets rich in vegetables, fish, nuts, whole grains, and omega-3 appear to be protective against cognitive damage. These foods are high in vitamins and antioxidants that can help counter the effects of oxidative stress on the brain caused by environmental pollutants. Eating more seafood is also linked to lower rates of dementia.
However, some debate exists over the links between diet and brain pathology. Some researchers point out that while it is well-documented that healthy eating can reduce the risk of developing certain diseases, further research is needed to quantify the amount or frequency of specific foods necessary to have a positive impact on the brain. Further debate surrounds the concept of brain-boosting foods — the interactive effect between nutrients in a single food or in multiple foods—which is not completely understood.
Therefore, while it appears likely that following a healthy diet is beneficial for maintaining good mental health, additional studies need to be conducted to delineate which dietary elements are most important for optimal mood and memory.
By focusing on eating habits and lifestyle changes, people can take greater control of brain chemicals and reduce their risk for diseases associated with poor dietary choices. This is the focus of the next section.
When it comes to healthy brain and nerve cells, the biggest determining factors are the diet and lifestyle habits we choose to follow. Eating a balanced, nutritious diet that contains a variety of foods from all the food groups is essential for optimal brain health. Eating too much processed or ‘junk’ food can harm our cognitive abilities and increase our risk of developing dementia and other age-related cognitive damage.
In addition to eating well, including plenty of physical activity in our daily routine is also important. Daily exercise helps improve our mental clarity and sharpness, increases blood supply to the brain, and releases chemicals called ‘neurotrophins’ which help preserve neurons and connections between them in the hippocampus – an area of the brain known to be involved in storing memories. Evidence suggests that even just 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per day can provide notable mental benefits.
Although these dietary and lifestyle changes may seem simple, making them part of our daily routine can be especially challenging. It’s important to remember that it takes commitment and consistency for results to be seen. Incorporate healthy behaviors into your lifestyle gradually rather than trying to make drastic changes overnight. This way we can ensure that we have sustainable long-term improvements in our overall well-being, not just for cognition but also when it comes to physical health.
As research has shown, a healthy diet is vital when it comes to maintaining a healthy brain. Consuming a balanced diet consisting of a variety of nutritious foods helps to keep the brain functioning optimally and can even help to reduce the risk of developing certain mental illnesses and neurological disorders such as dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, eating healthy foods helps to maintain overall physical health, which can have an indirect effect on the brain and heart, as good physical health has been linked to improved mood and emotional well-being.
The most brain-healthy foods are omega-3, B vitamins, vitamin D, and antioxidants. Omega-3 fatty acids help protect brain cells from damage and also play an important role in neurotransmitter function. B vitamins are essential for DNA replication and energy production within cells. Vitamin D is important for neuron growth and protection from inflammation, while antioxidants such as vitamin C help protect against oxidative stress caused by free radicals that can lead to cell damage.
A healthy diet plays an essential role in maintaining the optimal health of our brains. A balanced diet rich in omega-3, B vitamins, vitamin D, vitamin E, antioxidants, and other best foods can help reduce the risk of cognitive damage and ensure the brain functions optimally throughout life. Moreover, boosting one’s physical health with regular exercise has also been linked to improved mood, mental clarity, and more resilient neural networks which make it easier to tackle everyday stressors. All these factors combined make it evident that following a healthy diet is key when striving for peak mental performance.
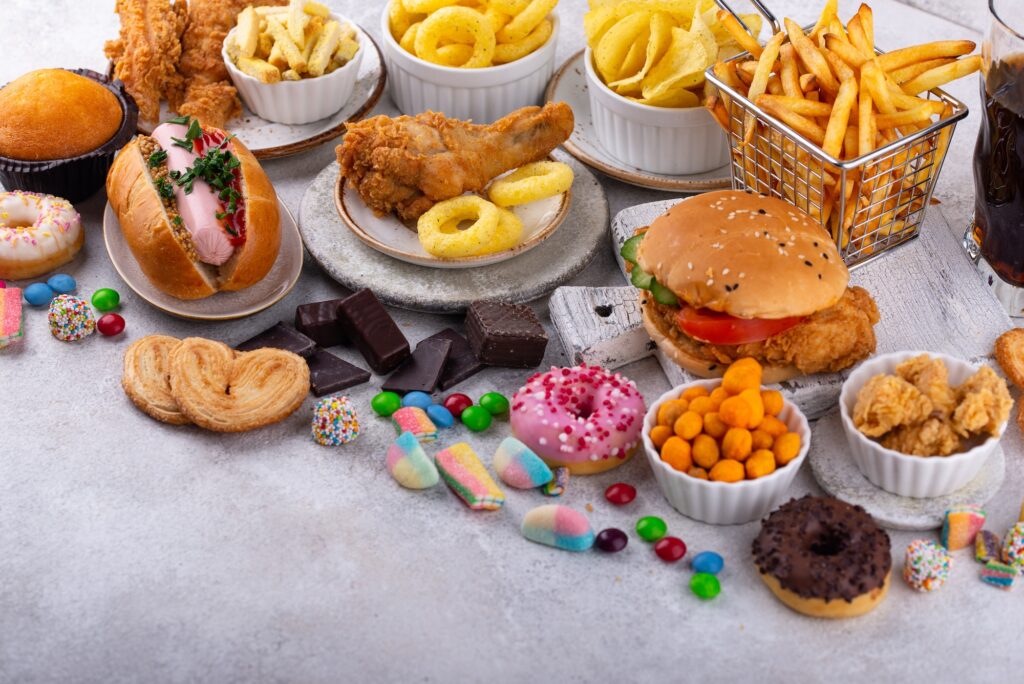

Yes, certain unhealthy foods can harm the brain. Some of these include highly processed food items such as candy, chips, and fast food, which are high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. These kinds of foods can reduce cognition, increase inflammation, and increase the risk of stroke and other conditions that can lead to memory loss or impaired thinking. Additionally, sugary drinks such as sodas provide empty calories without any nutritional benefits and can further increase the risk for obesity and diabetes—both of which can lead to cognitive decline. By avoiding these unhealthy food items, you can help your brain stay healthy and function optimally.
Several specific vitamins and minerals are important for brain health, including omega-3, B vitamins (such as folate, thiamine, and B12), choline, iron, zinc, and magnesium.
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining a healthy brain. Studies have shown that they can help protect against cognitive decline by reducing inflammation in the brain and increasing cognition. They can also be beneficial for depression and anxiety. Sources of omega-3 include fish oil supplements, salmon, tuna, and other fatty fish, flaxseed oil, and walnuts.
B vitamins play an important role in brain health, as they are involved in the metabolism of energy in the body and help to produce neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. Deficiencies in B vitamins can lead to poor memory, confusion, and fatigue. Folate is particularly important for pregnant women to ensure their baby’s brain condition is on track. Good sources of B vitamins include starches such as rice and potatoes, fortified cereals, eggs, and dark leafy greens like spinach.
Choline is another nutrient that is important for cognitive performance. It helps the body produce acetylcholine which is essential for learning and memory functions in the brain. Good sources of choline include eggs, beef liver, soybeans, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower.
Iron plays an important role in delivering oxygen to the brain cells and ensuring proper cognition. Iron deficiency can lead to fatigue and difficulty concentrating due to a lack of oxygen supply to the brain cells. Good sources of iron include red meat, lentils, tofu, spinach, and pumpkin seeds.
Zinc is essential for the formation of healthy neural connections in the brain which translates into improved cognition. Zinc deficiency has been linked with depression so it’s important to make sure you’re getting enough through your diet or supplementation if needed. Good sources of zinc include red meat, poultry, beans, and nuts.
Finally, magnesium helps regulate levels of glutamate in the brain which can be linked with Alzheimer’s disease when they become too high or low. Magnesium also plays a role in nerve signaling throughout the body which helps modulate learning ability so it’s important to get adequate amounts from your diet or through supplementation if needed. Good sources of magnesium include legumes such as peanuts and beans as well as cashew nuts, almonds, pumpkin seeds, and dark chocolate.
Not following a healthy diet can have serious implications on brain health. A diet high in processed and unhealthy foods can result in nutrient deficiencies that affect the brain, while an excess of unhealthy food can lead to weight gain, increased risk of hypertension, and a decrease in metabolic efficiency that strain the body. All of these negative factors can contribute to impairments in cognition and mood regulation, including memory problems, difficulty concentrating, problems with learning and reasoning, and even depression-like symptoms. Additionally, a diet lacking essential vitamins and minerals can impair blood flow to the brain, leading to reduced energy levels and a lack of motivation. Furthermore, diets high in saturated fats can clog arteries leading to the brain – reducing blood flow to the brain and increasing one’s risk for stroke. Ultimately, people eat for better performance with meals full of nutritious fruits, vegetables, proteins, and carbohydrates to protect the health of their brains.

Menopause support complexes are dietary supplements with herbal extracts and vitamins aimed at alleviating symptoms during menopause

Vitamin C, D3, Zinc, and Quercetin support immune health. They enhance immune cell function, fight infections, reduce inflammation, and provide antioxidant benefits.

Ginseng, a valued herb with adaptogenic and antioxidant properties, is popular as a supplement for improved well-being, energy, and immune function.

Nootropic supplements enhance focus, memory, and cognitive function. They boost mental clarity, motivation, and creativity for improved performance and brain health.

Garcinia cambogia, a tropical fruit, is touted for weight loss. Its active ingredient, HCA, may inhibit fat formation, but evidence is limited. Consult a professional before use.

More and more people are jumping on the mushroom supplement bandwagon these days, but you should be aware that there are potential side effects you should know about before taking the plunge. Whether you’re begging for overall well being or looking for an extra performance boost, you’re going to want to make sure you’re making an informed decision before adding mushroom supplements to your daily routine. We’ve put together a list of potential side effects to look out for, so read on and learn the truth before you start popping those pills.

Moringa, the “miracle tree,” offers numerous benefits. Moringa supplements provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory effects, and potential blood sugar and cholesterol regulation. They support immunity and combat malnutrition, but medical advice is essential.
It’s a good thing that Mother Nature both created and found cures for many of the ailments we humans suffer from. From the common cold to serious diseases, herbs have the potential to not only alleviate symptoms, but to completely prevent illnesses in the first place! Herbal remedies for immune system support have become increasingly popular as natural ways to boost your immunity against illness start to catch on.
